Windows Server Deployment Proposal
This IT proposal is tailored for Worldwide Advertising, Inc. (WAI), an advertising firm that is undergoing expansion. The firm is currently establishing its presence in two new locations and is in dire need of having the necessary Windows network infrastructure installed. The new subsidiary will employ 90 employees in both locations which have been identified as Chicago and Dallas. WAI does not have any cost concerns but wishes to have a workable IT solution. The Windows Server 2012 will be used to provide an IT solution. The success of an IT deployment project largely depends on planning and execution of the various tasks. This paper provides guidelines regarding the implementation and configuration of Windows Server at Worldwide Advertising, Inc.
New Features of Windows Server 2012
There are a number of enhanced and new features in Windows Server 2012 that can significantly improve efficiency and datacenter capacity (Ferril, 2013). This can make the business perform even better. Windows Server 2012 is suitable because it can provide a network that is distributed geographically, enabling firms to easily manage subsidiaries in different physical locations. In this case, the firm must be able to install a separate connection source meant primarily for the Windows Server. This is necessary so as to make easy the distribution and configuration administration process. The Windows Server2012 contains a number of other important features that are applicable in remote office settings. Some of these features include BranchCache, Remote Server Administration, and DFS Namespaces. Windows Server 2012 also has useful features that enable networks maintain safe communications in the on and off durations. This feature enables the server to maintain connectivity with multiple sites and other hosting providers. The highlights of the Windows Server 2012 Hyper—V are mainly enhanced Hyper-V model, rapid live relocation, online VM dissemination as well as cloning, and cleaner and trimmer “Gen2” attributes (Ferril, 2013).
Related: Desktop Virtualization
Deployment and Server Editions
A minimum of two physical Network Interface Cards (NIC) will be employed. The CPU requirements for HOST1 are 2 sockets with multiple cores for each socket. This will require a memory of 48 GB and a hard disk of 1TB. This should be divided into two partitions, the C drive having 120GB of free space and the rest allocated to the remaining drive. Under HOST2, the user requirements are similar as discussed above. Thus in sum, two servers will be required for better performance. The primary network adapter settings can be established by comparing to the current external network environment. A secondary network adapter will be used to enhance connectivity between private network hosts. A crossover cable is used to enhance direct contact between the two (Scarfone, Jansen, & Tracy, 2012). The servers will be located at Chicago since more staff will also be located there. It will be easy to extend the networking requirements to the Dallas site which will have fewer staff and hence less network requirements.
The Datacenter Windows edition will be employed because it is the best in terms of allowing unlimited simulated occurrences on all virtualization machines hosted on Windows Server 2012. Windows Server 2012 can best work with the servers since they have greater stability associated with lower running processes and also less likelihood of an improper configuration occurring. Datacenter windows edition is easy to design and ensure a Server Core Installation. The Server Core will in turn reduce the cost of maintenance that is associated with fixes of various binaries such as hotfixes and other security updates. It also reduces disk and memory requirements. Use of datacenters is advantageous since it reduces the need for conducting dynamic changes to the physical network infrastructure as they have the capacity to isolate tenant resources. This is possible because the datacenter edition supports multi-tenant virtualization. Datacenters can integrate multiple virtual networks irrespective of whether their IP addresses are overlapping over the same network.
Server Core will be used on both servers. A Server Core installation is required for a complete installation of the Windows Server 2012. However, there is no special hardware required during the installation. Servers will be deployed automatically. This will be made possible by downloading the Windows PowerShell Scripts that can aid in installing and configuring virtual machines.
Active Directory
Active Directory can be employed in configuring the MSI installer. This method enables multiple machines to be updated roughly the same time. Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) enables the programmers to install a distributed directory and database services that enable storage and management of information concerning users, groups, computers, printers, shares, and other objects within the IT infrastructure of the organization. Active Directories should be a minimum of two. A minimum of two domain controllers is required for effective performance. Two domain controllers can be able to run all the virtual machines in the organization. The two should be installed in different physical hosts. This ensures that a single computer failure does not cause problems to the entire directory.
Read-only domain controllers (RODCs) will be installed since they are critical in this kind of an environment. RODCs are employed in branches that have few users and no IT staff. The branches at Chicago and Dallas will operate with only a few IT staff which makes it necessary to install RODCs. RODCs are also suitable in areas that have slow WAN connectivity with the headquarters and in environments that have less physical security controls compared with those found in the headquarters (“Microsoft Corporation,” 2013).
The AD sites can easily be configured in this type of system. In every network, there are two topologies found: the logical topology and the physical topology. The physical topology is made up of network structure which involves items such as IP address allocations, network topologies, and hardware placements. Logical topology can be defined as the security boundaries of a particular network. Active Directory sites will be configured using the following setup.
| Server | Roles | Operating System | Site | Subnets |
| HOST1 | Primary domain controller | Windows server standard 2012 R2 | Chicago Site | 192.168.148.0/24 |
| HOST2 | Secondary domain controller | Windows server standard 2012 R2 | Dallas Site | 10.10.10.0/24 |
HOST2 will be situated in the Dallas site where there is less staff. It is important to note that both sites are in different geographical locations and hence there is need to connect the Dallas site to the primary domain through 256kb link. This will be setup in the default AD site.
In order to start the configuration setup, it is necessary to first log in to the primary domain controller. It is important to ensure that the user account used to start the configuration is registered under domain admin or as an enterprise admin. The sites should be clearly be identified and relevant servers assigned to each of them. The configurations should be handled under the services and the Active Directory Sites mmc. Both servers should be installed under the default AD site. This should be followed by the creation of a new site, which includes assigning the site names in the object field, and the selection of the link for the site. This marks the end of the process of creating the site. Similar steps are repeated when creating the second site. After the site is created, the next step is to develop the subnets. These are created for both sites (“Microsoft Corporation,” 2013).
The second site should factor into the domain controller placement. This can be achieved through a number of steps. After the site configuration and the link setup, the domain controllers are placed into the relevant sites. The Active Directory Sites and Services in the mmc enables one to place the domain controllers in the respective sites. The developer can be able to move the server to any site that he/she wishes by following a number of steps. The default field enables the developer to identify the position to place the domain controllers, either in the first or second site.
It is critical to design an organizational unit structure that fits and reflects the needs of the organization. In group policy, the organizational unit must take into consideration the type of group objects that will be employed to the organizational unit. A group policy object enables the developer to configure various settings for users in an easy manner. For instance, it is possible to establish multiple group policy objects in the Active Directory and then apply these to the entire range of domain. User policies as well as computer policies can be established in a single group policy object. The organizational unit will be arranged in such a way that it is in line with permissions given in the domain. Thus if a particular user have full control of a computer, then the user should be able to make modifications of a number of attributes concerning the object (Ken, 2008).
DNS and DCHP
The DNS and DHCP are among the core network services. When implementing the DHCP, an IP addressing scheme must be established. This should contain the same number of IP addresses coinciding with the actual number of all devices in the organization. The DCHP should be configured using a scope that can support more than 100 clients. The subnets should be divided among a variety of DHCP servers. This will enhance maximum redundancy of the IP scope. Since the organization will have about 90 users, a scope in the range of 192.168.x.x can be used (Bird, 2014). This can be implemented in case where two servers are deployed and can support a maximum of 127 devices. It will be necessary to apply fault tolerance on the DHCP. Domain controllers can be used to offer fault tolerance in DHCP servers. There may be problems with the existing hardware which may fail to support DHCP. IP address scopes should not be switched when the DHCP server is being introduced as this may present problems. A dynamic host configuration protocol can be used for the servers to ensure a smooth reregistration of users with WINS server in case hitches occur.
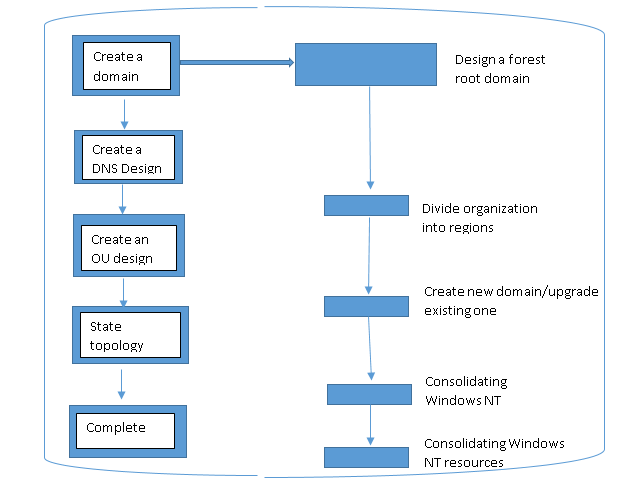
The design of the Domain Name System (DNS) with regard to its implementation in an Active Directory Scenario is supposed to first take into consideration the directory environment before implementing a DNS structure. A DNS namespace is first established when implementing the DNS namespace layout. It is also important to implement the child domains as subsidiary within the DNS namespace and with respect to their parent fields. A split DNS configuration is suitable in this case in order to enhance integration with internal hosts. This enables naming of the internal domain server. External hosts should be integrated with an external domain server which can enable name resolution.
Figure 1.1: Establishing a domain design
Application services
Group Policy as well as Remote Installation services (RIS) has shortened the time taken by the developers to fit applications and systems. An automated operating system can significantly help in reducing the administration overhead incurred when fixing applications in manual operating systems (Tulloch, 2012). Group Policy can save on time especially there is deployment of new systems. This can occur when an upgrade occurs and affects the users. A user OS often accompanies the installation of a new system. This makes it necessary to design various items such as documents, public templates, and instituting applications. Group Policies can considerably reduce the amount of time required to set up the OS since it helps in slipstream fixing of various service packages. An important application in this will be OEM-fixed OS. A disk-imaging software can be applied in installing the OS especially when the hardware in the two sites is similar. After installing the OS, all applications in high demand by users are fixed. This may take more time due to complexity issues.
File and Printer Sharing
There are a number of file and printer sharing required. These include public folder sharing, home groups sharing, and individual folder sharing. Public folders are important because they enable users with log it credentials to access files and documents placed in public folders. In individual folder sharing, not everyone who has login credentials can access files and documents. This type places more stringent measures to access or control a particular folder. In a home group, a panel of computers are allowed to share documents and folders. Network and servers allow users in a system to share files, documents, and printers. Windows Server 2012/R2 has various features that enhance sharing of files, documents, and printers (Tulloch, 2012). The DFS is a critical tool in enhancing file sharing and hence will be employed. The FSRM is of great importance designing storage quotas. It greatly helps in organization of files stored on the file server. The configuration of FSRM is conducted by picking up the Add roles and Feature instructions from the Server Manager. Other features may also be included for easier management of the File Server.
References
Bird, D. (2014). The simplicity and serenity of DHCP fault tolerance. eSecurity Planet.
Ferril, P. (2013). 10 excellent new features in Windows Server 2012R2. Infoworld.
Ken, C. (2008). Designing OU structures that work. TechNet.
Microsoft Corporation. (2013). Windows Server 2012 R2 Evaluation Guide. Retrieved from: https//www. windows_server_2012_r2_evaluation_guide.pdf
Scarfone, K., Jansen, W., & Tracy, M. (2012). Recommendation of the National institute of Standards and Technology. NIST.
Tulloch, M. (2012). Installing and Configuring Windows Server 2012. Microsoft Corporation.
Related: Intranet project and Self-service portal system for Dingwow Inc.