Question
PowerPoint presentation that discusses the decision making process in a criminal justice organization. Base the presentation on a Criminal Justice organization you are familiar with from personal experience or select an organization through research.Discuss the decision making model and processes that pertain to the organization you selected.
Provide an organizational chart to demonstrate the organization’s structure.
Sample paper
Decision Making Process in ACA
American Correctional Association
- The American Correctional Association (ACA) was founded in 1870.
- ACA is an accrediting body in the corrections industry.
- ACA helped introduce prison reforms in the 1960s.
- ACA has also helped in prison expansion.
- Helps in developing and implementing standards.
Founded in 1870, the American Correctional Association (ACA) has been at the forefront of prison reforms and expansion in the United States (American Correctional Association (ACA), 2016). ACA acts as an accrediting body in the corrections industry. The ACA was the first justice organization to publish standards manuals before the accreditation program was in place. In the 1960s, ACA established and helped to implement national correctional standards across U.S. prisons. This came after an increased pressure from courts for prison reforms. The major aim of these reforms was to implement the best possible standards or practices in prisons across the U.S. ACA standards guide the development of policies and procedures that are critical in formulation of correctional programs that deal with the welfare of inmates.
Scope of ACA
- Juvenile institutions
- Adult institutions
- Higher learning institutions.
- Community corrections.
ACA is a nonprofit and nongovernmental organization in the corrections industry. It acts as a professional membership organization whose major aim is to improve the general state of corrections (ACA, 2016). The professional body also aims at improving the quality of service provision by correctional professionals through training and development. ACA extends its mandate to a number of corrections systems, which include juvenile institutions, adult institutions, higher learning institutions, and in community corrections.
Departments in ACA
- Membership and Financial Services Department.
- Publications and Professional Development.
- Conferences Department.
ACA has a number of departments each charged with a specific responsibility or service. The professional body has six departments that provide a variety of services. The first department is Membership and Financial Services department. This department coordinates various services such as membership and renewal of the same, chapters and affiliates, and student information for the students under ACA. The second department is Publications and Professional Development. This department is responsible for making publications of standards and other reports as well as ensuring training and development of employees. The third department is the Conferences department, which oversees the workshops and conferences (ACA, 2016).
- Advertising and Corporate Relations department.
- Correctional Health Care Department.
- Global Corrections department.
The fourth department is Advertising and Corporate Relations department. This department deals with the media and other bodies to enhance the public image and to pass important information to the public. The Correctional Heath Care department oversees the accreditation of health care programs through certification. The Global Corrections department oversees various activities such as outreach programs, international scholarship programs, internship programs, and among others (ACA, 2016).
Ethical model
- ACA utilizes ethical model of decision making.
- Ethical model emphasizes on a logical procedure to a rational procedure.
- Business ethics determine the performance of the organization.
The American Correctional Association uses the ethical model of decision making. The ethical model emphasizes on a logical procedure in decision making rather than rational procedure (Verma, 2014). The ethical decision model gives the individuals involved in decision making the autonomy to develop decisions. In ethical decision making, the parties involved focus on developing solutions that are not harmful to others. By utilizing a systematic model in decision making, policymakers are able to provide rationale for choosing a particular plan of action. The ethical model of decision making is of great significance to organizations. Business ethics are core essentials in any organization, impacting the entire organization from the lower levels to the upper managerial levels (Verma, 2014). Business ethics determine the performance of an organization. When there is poor conformance to ethics, the organization may perform poorly due to unethical practices some of which may undermine the image of the organization to the public.
Procedure in Ethical Decision Making
- Identification of the problem.
- Analyzing ethical codes.
- Examining laws and regulations.
Individuals involved in ethical decision making follow a certain procedure in identifying solutions to various challenges. The first step is to identify the problem and to evaluate the potential issues surrounding the problem. Potential issues affecting the problem may include duties, rights, and welfare. The second step involves analyzing the ethical codes surrounding the identified problem. The next step involves examining the various local or national regulations affecting the problem. In case the decision makers lack adequate knowledge concerning the ethical issue at hand, they can consult professionals who may shed more light about the problem.
- Analyzing possible solutions.
- Analyzing the consequences of each solution.
- Evaluate the selected option.
- Implementation.
The next step involves analyzing the possible solutions and consequences involved. When there are significant consequences to a particular solution, the best alternative is to examine other possible solutions which have less severe consequences. The selected solution should bear three distinct characteristics that include universality, publicity, and justice. Lastly, the decision makers must settle on the best alternative. The implementation stage involves ensuring that the selected course of action is implemented (Verma, 2014). This stage also involves analyzing the possible problems that emerge from the implementation of the selected course of action.
Core Mandate
- Developing standards and accreditation.
- Oversight in the country’s prisons, jails, correctional facilities, and juvenile detention centers.
- Publishing correctional standard manuals.
The American Correctional Association is mainly involved in formulating standards and the accreditation process. The body ensures there is higher oversight in the country’s prisons, jails, correctional facilities, and juvenile detention centers (Bogard, 2010). ACA publishes a variety of correctional standard manuals that guide different organizational types and programs. Over the last three decades, ACA has expanded its mandate to cater for development of institutional health care standards.
ACA organizational Chart
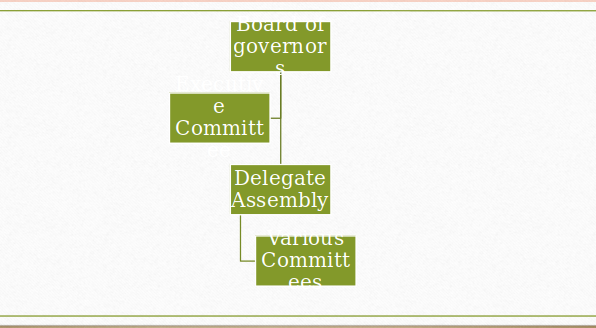
Chain of Command
- Board of governors
- Comprises of over 18 members.
- Executive Committee.
- Comprises of treasurer, president elect, vice-president, executive director, and other board members.
The linear organizational structure exhibited in the previous slide indicates the simple organizational structure employed by the American Correctional Association. The Board of Governors is the highest level of decision making. There is at least 18 board members who represent diverse areas of corrections such as juvenile, probation, parole, correctional administration, and others (American Correctional Association (ACA), 2013). The Board of Governors (BOG) makes crucial decisions regarding adoption and modification of various standards. The Executive Committee comprises of eight members. They include treasurer, president elect, vice-president, executive director, and other board members. The role of the Executive Committee is to exercise the powers of the BOG.
- Delegate Assembly.
- Comprise of members from geographical chapters, board members, professional affiliates, and past presidents
- Committees.
The Delegate Assemble is made up of members drawn from geographical chapters, board members, professional affiliates, and past presidents (ACA, 2013). The Delegate Assembly is charged with a number of roles including policy establishment, determining key programs, defining legislative priorities, and establishing ACA’s position on various professional issues. At the bottom of the chain, there exist different committees. The committees chair reports and helps in formulation of standards. The committee comprise of many individuals who collectively contribute towards decision making and policy enactment.
Decision Making
- Standards Committee is in charge of decision making.
- The committee comprise of members from diverse sectors of corrections.
- An active solicitation process informs decision making.
The American Correctional Association has established a Standards Committee that is in charge of decision making. The Standards Committee is made up of about 20 members with diverse correctional knowledge and expertise. The members yield diverse expertise on jail administration, community corrections, consultation, and in other areas. The Standards Committee makes crucial decisions on whether to adopt new or revised standards (ACA, 2013). Meetings are held twice a year. Extensive consultation from relevant individuals in the corrections systems inform the committee of whether to adopt the new standards or to dismiss them. Consultations also enable the committee decide on whether to accept modifications of existing standards. A solicitation process in the field enables the Standards Committee to identify the need for new standards or the need for modification of preexisting standards.
Bodies contributing to new standards
- Prisoner advocacy organizations.
- Facility managers.
- Various architects.
A number of individuals or bodies in the corrections may generate changes to standards within the industry. Prisoner advocacy organizations are some of the bodies that recommend various changes to standards (Bogard, 2010). Once the advocacy organizations make recommendations, the Standards Committee evaluates them and makes decisions on whether to implement the recommendations. Facility managers also make recommendations. Facility managers are in charge of various correctional organizations. As such, they are able to provide useful information concerning the areas that need changes. Various architects also make recommendations about appropriate standards (Bogard, 2010). The corrections systems may consult various professionals involved in developing and implementation of changes in the corrections system.
- Physicians and other healthcare workers.
- Commission members.
- Consultants.
Physicians also add significant value to the standards development process in corrections. Physicians and other healthcare workers who provide health services in jails and prisons provide important recommendations regarding health standards. Physicians generally help in improving the living conditions in prisons to reduce transmission of diseases. The accreditation commission members also provide insights into the improvement of correctional facilities. Commission members add their individual expertise into the development and modification of standards. Another important source of insight into standard development relates to consultants. Various consultants may provide useful recommendations on improving or modification of standards. Consultants have knowledge and expertise on various issues touching on correctional facilities in the country.
Considerations during the Decision Making Process
- The proposals must be serving the interests of the correctional facilities.
- Implementation costs.
- Adherence to federal and state regulations.
The decision making process is an intricate and complex process. The decisions by the Standards Committee undergo rigorous checks to ensure they promote the general welfare in correctional organizations (Bogard, 2010). As such, the decisions are subject to robust discussions in order to determine their efficacy. Various debates are held in order to examine the strengths as well as the weakness of each decision. The main agenda during such debates is to examine whether the proposals made serves the interests of various correctional facilities. The cost of implementing a particular standard is a critical determinant in deciding whether to implement the particular proposals or standards. The cost implications of various standards may make it impractical to implement the standards. Another important consideration pertains the adherence of the proposed standard to federal regulations or statutes. The attorneys may not accept a standard that violates federal or state laws.
Conclusion
- The decision making process is a critical success factor.
- Good decision helps improve practices.
- ANA uses an ethical model in decision making.
The decision making process is a key component in the success of an organization. In criminal justice organizations such as American Correctional Association, decision making has played a pivotal role in ensuring the implementation of new standards in correctional facilities. Application of robust decision making approaches has enabled ACA to improve practices in various correctional organizations such as Juvenile institutions, adult institutions, higher learning institutions, and community corrections. The American Correctional Association uses the ethical model of decision making. The ethical model emphasizes on a logical procedure in decision making rather than rational procedure.
References
Bogard, D. M. (2010). Effective corrections oversight: what can we learn from ACA standards and accreditation? Pace L. Rev., 30(5): 17. Retrieved from http://digitalcommons.pace.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1760&context=plr
American Correctional Association (ACA). (2013). Accreditation Report. Retrieved from http://bopp.mt.gov/Portals/42/about/Accreditation_Letter_and_Report_2013.pdf
American Correctional Association (ACA). (2016). About us. Retrieved from http://www.aca.org/aca_prod_imis/aca_member
Verma, D. (2014). Study and analysis of various decision making models in an organization. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 16(2): 171 – 175.